GENETIC ENGINEERING IN AGRICULTURE
The Restoration of Food

BACKGROUND INFORMATION
Rna interference
Ribonucleic acid interference is one of the four methods used to genetically modify crops, others including traditional breeding, mutagens, and transgenic. This technique was introduced by Nobel Prize winning scientists, Andrew Z. Fire and Craig C. Mello in 2006. Both scientists first found RNAi when inserting worms with sense and anti RNA combined, resulting in movements in the organism. RNAi also has the job of aiding in development and fighting viruses, but it is mainly known for having the ability to suppress genes.
RNAi executes this by interfering with messenger RNA from reaching protein making factories within the cell, thus silencing the production. Additionally, RNAi can target specific proteins, for example, proteins that contribute to the pigmentation or oil concentration of plants, proving it to be a powerful tool in agriculture. RNAi could be applied using various techniques, those including synthetic molecules, RNAi vectors, and vitro dicing. Read more about how RNAi works
[B.1]

[B.5]
The impact
RNAi interference could dramatically increase the production of produce. However, this tool could also be used to aid in diseases by turning off single genes, propelling biomedical research instead of just being used in agriculture. By having the ability to silence genes, scientists are able to learn about its functions to utilize their findings for the better of the public. RNAi is efficient in targeting pests that deteriorate valuable crops, proving it to be a breakthrough method that feeds and treats the world.
[B.2]
Overview of Bacillus thuringiensis
Bacillus thuringiensis is classified as a gram positive bacteria and is among the bacilli shaped family, differing from cocci and spirals. Found from tundras to deserts, this bacteria was found to be efficient in products like corn and cotton. BT was first discovered by a Japanese scientist due to investigating the alarming decline in silkworm moths. It was first used as a pesticide during the 1920's and is moreso used in organic farming today.
Additionally, the significant role it plays is producing toxic proteins that are encoded by Cry genes, found on the plasmid. Many strains of BT during formation of spores have found to produce these specific proteins. Additionally, endospores allow bacteria to become dormant, or inactive for a long period of time and sustains itself without nutrients. They also help better the understanding for gene expression and is used in fields like microbiology and biotechnology.


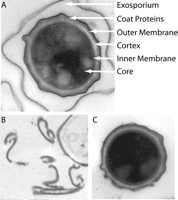
[B.3]
[B.6] Here displays various groupings of bacteria.
[B.7] [B.8] Here displays the structure of BT.
BT crops
After the discovery of bacillus thuringiensis, scientists realized its potential. Today, BT crops are now used the method of transgenic to genetically modify organisms. This method aids with the estimated 20-40% crop failure and pesticide use that cost setbacks to agriculture and damaging the environment. The technique of transgenics is performed by inserting selected genes into another organism, altering its genome in the process. By inserting crops with this bacteria, it produces Cry proteins that's toxicity is potent and efficient in dismantling insect larvae. This type of pesticide is also called biopesticide, differing form microbial, plant-incorporated, and chemical pesticides, the most commonly known category.
[B.3] [B.4]

Although harmful to others, BT crops are safe to consume for humans due to the absence of digestive enzymes that insects have to activate the toxins. Additionally, this crop does affect honeybees and other pollinators critical to the daily lives of all organisms. However, worry about insect resistance has sparked and many wonder how the effectiveness of BT crops would alter. Read more about the issues
[B.9]
The impact
BT crops play a significant role in the world of agriculture, feeding the world without harmful chemicals spreading throughout the atmosphere. Conditions associated with the use of chemical pesticides include cancer, damage to the endocrine, nervous, and reproductive system. BT crops are safe to humans and consumption of certain mammals and only had two incidents before 1995 that show minor complications like skin sensitization. By having the ability to combat rootworm, tobacco budworm, bollworm, and more, the increase of produce can skyrocket.


[B.4]
[B.10][B.11] Here these image demonstrates the difference between the use of BT and without.
challenges
Challenges faced when encountering the the use of GMOs include the negative conception around it. With organizations working to promote the use of non-GMO products like the Non-GMO project, a widely known cooperation, GMOs are presented in a negative light. Many other companies are joining in to combat the growing popularity of GMOs and the sales contributing to the technology. To learn more about other issues, including social, legal, and ethical, click
[B.13]
pros and cons for gmos
GMOs are controversial to many, even banned in specific countries like Russia, China, Italy, Mexico, France, India, and more. In total twenty six countries have banned GMOs due to the negative stigma surrounding the technology.

Pros
-
Greater amount of produce: Extended shelf life and new features make GMO products more sustainable than ever. This results in a decrease of produce being wasted, feeding more people in the process.
-
Use of fewer pesticides: Health risks of citizens and the environment will greatly benefit from this technology. Water that was once affected by pesticides can decrease along with severe health defects associated with pesticides like cancer.
-
Less maintenance: Crops are able to be modified to harvest in greater conditions including saltwater, droughts, and hotter/colder temperatures. This will cut down costs of maintenance while also decreasing the time spent on caring for these crops.
-
New features in crops: The ability to add a greater nutritional value like proteins and calcium are also beneficial. Seedless fruits are also a new feature that consumers are able to purchase, grapes and watermelon being examples.
Cons
-
The creation of superweeds: Superweeds can uncontrollably spread and are difficult to exterminate. The effect superweeds can have on other crops could be a potential problem.
-
Insect resistance: Insects have the ability to adapt to resistance crops quickly. This leads scientists to struggle about how to deduce this process, preserving our crops in the end.
-
Allergies: The allergy rate of of children under the age of eighteen has lead some to suspect the correlation between allergies and GM crops. The concern is found in the transferring of varying proteins between other crops, creating the potential to stimulate allergies.
[B.12]
[B.13]
[B.13]